Book of Daniel
The Book of Daniel (Hebrew: דניאל) is a book in the Hebrew Bible originally written in Hebrew and Aramaic. The book revolves around the figure of Daniel, who tradition holds wrote the book. The book in part tells the story of how Daniel, a Judean, becomes chief of the magicians (4:9) in the court of Nebuchadrezzar II, the ruler of Babylon from 605 to 562 BCE during the Babylonian Captivity, a period when Jews were deported and exiled to Babylon following the Siege of Jerusalem of 597 BCE. In contrast to the traditional belief that the book was written around the time of those events,[1] Most modern biblical scholars figure that the Book of Daniel was likely written or redacted during the Maccabean Age[2][3][4] and that "the arguments for a date shortly before the death of Antiochus IV Epiphanes in 164 are overwhelming."[5] Some scholars, however, are less definite, suggesting that "the most likely time of composition is somewhere between the beginning of the second century BCE and the coming of Pompey"[6] and that "evidence for a more specific date is not available."[6] Mangano argue for a third or fourth century date.[7]
The book has two distinct parts: a series of six narratives (chapters one to six) and four apocalyptic visions (chapters seven to twelve). The narratives take the form of court tales which focus on tests of religious fidelity involving Daniel and his friends (chapters one, three and six), and Daniel's interpretation of royal dreams and visions (chapters two, four and five). In the second part of the book, Daniel recounts his own reception of dreams, visions and angelic interpretations in the first person. Since modern biblical scholarship dates the book to after Daniel's time, predictions of the book accordingly may refer to events that had already occurred (ex eventu) even as the prophetic chapters of Daniel figure prominently in the teaching by fundamentalist religious believers in the text as an example of biblical prophecy.[8]
Contents
|
The Court Tales
|
Part of a series
of articles on the |
|---|
| Tanakh (Books common to all Christian and Judaic canons) |
| Genesis · Exodus · Leviticus · Numbers · Deuteronomy · Joshua · Judges · Ruth · 1–2 Samuel · 1–2 Kings · 1–2 Chronicles · Ezra (Esdras) · Nehemiah · Esther · Job · Psalms · Proverbs · Ecclesiastes · Song of Songs · Isaiah · Jeremiah · Lamentations · Ezekiel · Daniel · Minor prophets |
| Deuterocanon |
| Tobit · Judith · 1 Maccabees · 2 Maccabees · Wisdom (of Solomon) · Sirach · Baruch · Letter of Jeremiah · Additions to Daniel · Additions to Esther |
| Greek and Slavonic Orthodox canon |
| 1 Esdras · 3 Maccabees · Prayer of Manasseh · Psalm 151 |
| Georgian Orthodox canon |
| 4 Maccabees · 2 Esdras |
| Ethiopian Orthodox "narrow" canon |
| Apocalypse of Ezra · Jubilees · Enoch · 1–3 Meqabyan · 4 Baruch |
| Syriac Peshitta |
| Psalms 152–155 · 2 Baruch · Letter of Baruch |
|
|
The first six chapters comprise a series of court tales involving Daniel and his three companions. The first account is in Hebrew; then Aramaic is used from ch. 2:4, beginning with the speech of the "Chaldeans", through chapter seven. Hebrew is then used from chapter eight through chapter twelve. Three additional sections are preserved only in the Septuagint, and are considered apocryphal by Protestant Christians and Jews, and deuterocanonical by Catholic and Orthodox Christians.
- After being taken captive to Babylon, members of the Israelite nobility are taken into the king's service. Among these, Daniel and his three friends (Shadrach, Meshach, and Abednego) refuse to eat and drink at the king's table because the food may be ritually unclean.[9] At the end of a short trial period they appear healthier than those who have accepted the royal rations and are allowed to continue with their abstemious diet of vegetables and water. Finally, after a three year induction, they enter the king's service and in matters of wisdom, literature, and learning are judged "ten times better than all the magicians and enchanters in the kingdom". Daniel, moreover, has a unique talent for interpreting dreams and visions. Despite apparent defeat and the ransacking of the Jerusalem temple, Israel's God is surprisingly active in this chapter: "deliver[ing]" the King of Judah into Nebuchadnezzar's hands, causing the chief official to treat Daniel and his friends favorably, and giving the four exceptional knowledge and understanding. Many of the book's key themes are introduced in this chapter.
- The king has a disturbing dream and asks his wise men to interpret it, but refuses to divulge its content. When they protest he sentences all of them, including Daniel and his friends, to death. Daniel intervenes and asks for a temporary stay of execution so that he can petition his God for a solution. He recevies an explanatory vision in the night, and then relays the content and meaning of the king's dream the following day. Nebuchadnezzar has dreamt of an enormous idol made of four metals, with feet of mixed iron and clay. The image is completely destroyed by a rock that turns into a huge mountain, filling the whole earth. The idol's composition of metals is interpreted as a series of successive kingdoms, starting with Nebuchadnezzar. Finally all of these dominions are crushed by a kingdom that will "endure forever".
- The account of the fiery furnace, in which Ananias (Hananiah/Shadrach), Azariah (Abednego), and Mishael (Meshach) refuse to bow to the emperor's golden statue and are thrown into a furnace. As seen by Nebuchadnezzar, a fourth figure appears in the furnace with the three and God is credited for preserving them from the flames.
- Nebuchadnezzar recounts a dream of a huge tree which is suddenly cut down at the command of a heavenly messenger. Daniel is summoned and interprets the dream as referring to Nebuchadnezzar, who for seven years will lose his power and mind and become like a wild animal. All of this comes to pass until, at the end of the seven years, Nebuchadnezzar acknowledges that "heaven rules" and his kingdom and sanity are restored. The recurring image of a tree representing a kingdom appears at least three times in the Bible.
- Belshazzar's Feast, where Belshazzar and his nobles blasphemously drink from sacred Jewish temple vessels, offering praise to inanimate gods, until a hand mysteriously appears to the king and writes upon the wall of the palace. The horrified king eventually summons Daniel who is able to read the writing and offer the following interpretation: Mene, Mene - God has numbered the days of your reign and brought it to an end. Tekel - You have been weighed on the scales and found wanting. Upharsin - Your kingdom is divided and given to the Medes and Persians. "That very night", we are informed, Belshazzar was slain and "Darius the Mede" took over the kingdom.
- Daniel is elevated to a pre-eminent position under Darius which elicits the jealousy of other officials. Knowing of Daniel's devotion to his God, these officials trick the king into issuing an edict forbidding worship of any other god or man for a 30 day period. Because Daniel continues to pray three times a day to God towards Jerusalem, he is accused and king Darius, forced by his own decree, throws Daniel into the lions' den. God shuts up the mouths of the lions and the next morning king Darius finds Daniel unharmed and casts his accusers and their families into the lions' pit where they are instantly devoured.
- Susanna and the elders (apocryphal to Jewish and Protestant canons)
- Bel and the Dragon (apocryphal to Jewish and Protestant canons) - Bel and the Dragon contains three interconnected court tales set in the reign of an unidentified "King of Babylon". In the first Daniel uncovers a trick by the Priests of Bel designed to promote a belief that the cult idol magically consumes food and drink offerings set before it each night. Daniel secretly scatters ashes on the floor of the god's locked chamber before it is sealed by the king and, in the morning, the incriminating footprints of the priests result in their slaughter and the destruction of the idol. In a second, Daniel feeds cakes made of pitch, fat and hair to a sacred serpent revered as a god which causes it to explode. Finally, the anger of the Babylonians at the destruction of their gods is directed towards Daniel with the result that he is thrown into a den of lions. During this time he is fed by the prophet Habakkuk who has been miraculously transported to Babylon for that very purpose. Finally the king rescues Daniel and has him replaced by his accusers who, as in the similar story of chapter six, are killed instantly.
Protestant and Jewish editions omit the sections that do not exist in the Masoretic text: in addition to the two chapters containing accounts of Daniel and Susanna and of Bel and the Dragon, a lengthy passage inserted into the middle of Daniel 3; this addition contains the prayer of Azariah while the three youths were in the fiery furnace, a brief account of the angel who met them in the furnace, and the hymn of praise they sang when they realized they were delivered. The Prayer of Azariah and Song of the Three Holy Children are retained in the Septuagint and in the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Roman Catholic canons; the "Song of the Three Holy Youths" is part of the Matins service in Orthodoxy, and of Lauds on Sundays and feast days in Catholicism.
The narratives are set in the period of the Babylonian captivity, first at the court of Nebuchadnezzar and later at the court of his successors Belshazzar and a 'King Darius' of unclear identity (see 'Historical Accuracy' and 'Date' below). Daniel is praised in Easton's Bible Dictionary, 1897, as "the historian of the Captivity, the writer who alone furnishes any series of events for that dark and dismal period during which the harp of Israel hung on the trees that grew by the Euphrates. His narrative may be said in general to intervene between Kings and Chronicles on the one hand and Ezra on the other, or (more strictly) to fill out the sketch which the author of the Chronicles gives in a single verse in his last chapter: 'And them that had escaped from the sword carried he (i.e., Nebuchadnezzar) away to Babylon; where they were servants to him and his sons until the reign of the kingdom of Persia' (2 Chr. 36:20)." However, see the section on Dating and Content (below) for other views on the dating and historical accuracy of the court tales.
Apocalyptic visions in Daniel
| Part of a series on |
| Eschatology |
|---|
|
Christian eschatology
Bibical texts
Book of Revelation |
|
Islamic eschatology
Places
Akhirah |
|
The Messiah
Book of Daniel |
|
Zoroastrian eschatology
Frashokereti (eschatology)
Saoshyant |
|
Inter-religious
End times
Apocalypticism 2012 phenomenon Millenarianism Last Judgment Resurrection of the Dead Gog and Magog Messianic Age |
The four visions of chapters seven to twelve are an early example of apocalyptic literature and, in contrast to the earlier chapters, are introduced in the first person. One feature of this section is Daniel's reliance on heavenly figures to interpret and explain his visions. The historical setting of the first chapters does not appear, except in the form of regnal dates. Chapter seven is written in Aramaic while chapters eight to twelve are in Hebrew. The "apocalyptic" sections of Daniel consist of four visions focusing on a fearsome future king who attacks the "saints", and the city and temple of Jerusalem:
Vision of the great beasts
The vision in the first year of Belshazzar the king of Babylon (7:1) concerning four great beasts (7:3) representing four future kings (7:17) or kingdoms (7:23), the fourth of which devours the whole earth, treading it down and crushing it (7:23). This fourth beast has ten horns representing ten kings. They are followed by a further wicked king, or "little horn", who subdues three of the ten (7:24), speaks against the Most High, wages war against the saints, and attempts to change the set times and laws (7:25); after 'a time and times and half a time', this king is judged and stripped of his kingdom by an "Ancient of Days" and his heavenly court (7:26); next, "one like a son of man" approaches the Ancient of Days and is invested with worldwide dominion; moreover, his everlasting reign over all kings and kingdoms is shared with "the people of the Most High" (7:27)
Vision of the ram and goat
The vision in the third year of Belshazzar concerning a ram and a male goat (8:1-27) which, we are informed, represent Media, Persia (the ram's two horns), and Greece (the goat). The goat with a mighty horn becomes very powerful until the horn breaks off to be replaced by four "lesser" horns. The vision focuses on a wicked king who arises to challenge the "army of the Lord" by removing the daily temple sacrifice and desecrating the sanctuary for a period of "twenty three hundred evening/mornings". Rams, goats and horns were used in the service of the sanctuary.
Prophecy of the seventy "weeks"
The vision in first year of Darius the son of Ahasuerus (9:1) concerning seventy weeks, or seventy "sevens", apportioned for the history of the Israelites and of Jerusalem (9:24) This consists of a meditation on the prediction in Jeremiah that the desolation of Jerusalem would last seventy years, a lengthy prayer by Daniel in which he pleads for God to restore Jerusalem and its temple, and an angelic explanation which focuses on a longer time period - "seventy sevens" - and a future restoration and destruction of city and temple by a coming ruler.
Vision of the kings of north and south
Daniel has a lengthy vision (10:1 - 12:13) in the third year of Cyrus king of Persia, regarding conflicts between the "King of the North" and the "King of the South" (= Egypt, 11:8). Starting with references to Persia and Greece it, again, culminates in the description of an arrogant king who desecrates the temple, sets up a "desolating abomination", removes the daily sacrifice, and persecutes those who remain true to the "holy covenant".
The king of the north is likely the Seleucid, also known as Syriac, kingdom which climaxed in Antiochus IV "Epiphanes" persecuting Jews in Judea and placing an idol in the Temple in Jerusalem.
The visions of Daniel, with those of 1 Enoch, Isaiah, Jubilees, Jeremiah and Ezekiel, are the inspiration for much of the apocalyptic ideology and symbolism of the Qumran community's Dead Sea scrolls and the early literature of Christianity. "Daniel's clear association with the Maccabean Uprising and those against Rome are a possible factor in the eventual downgrading of it, to include a redefinition of the role of prophet, keeping in mind that at roughly this time the Hebrew canon was being evaluated and adopted. (Eisenman 1997, p 19f).
In Daniel are the first references to the "kingdom of God", and the most overt reference to the resurrection of the dead in the Tanakh.
Literary structure
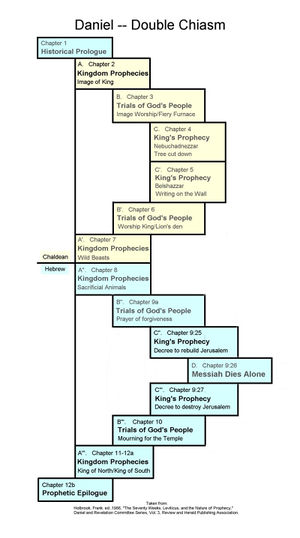
Seventh Day Adventist William H. Shea Ph.D. (Archeology).[10] suggests that the book of Daniel was composed as a double chiasm. Chiastic or concentric structure is a common feature of ancient Hebrew poetry and literature. A qualification, however, is appropriate: while the chiastic structure of chapters 2 - 7, originally identified by A. Lenglet in 1972, is widely accepted by scholars, Shea's proposal for a similar structure in chapters 8 - 12 is not.
Related themes have common label
Related sections have a common label. For instance those labeled A, A', A" and A"' are placed in parallel because they all have a similar theme: prophecies about successive kingdoms. God's people suffer trials in the parts labelled B, B', B" and B"', although the suggested parallels in chapters 9 and 10 seem to have little in common with 3 and 6. The decision of kings to choose Daniel's God or not are the themes in C, C', C" and C"', provided we can agree with Shea that two individual verses in chapter 9 are the structural counterparts of chapters 4 and 5. The trial faced by the Messiah is portrayed in the focal point of the book (D ) by Shea.
Language emphasizes structure
To emphasize the importance of the chiastic structure, the first chiasm was written in Aramaic and the second in Hebrew. The literary structure explains why Aramaic continues to be used in chapter 7 rather than ending in chapter 6 at, seemingly, the end of the first half of the book.
Structure has precedence over chronology
The literary structure of the book takes precedence over chronology. The first 6 narrative chapters are fit into the structure rather than defining it. For instance, chapter 6 ( B' ), which ought to follow chapter 7 ( A' ) chronologically, is put in parallel with chapter 3 ( B ) because they both deal with the persecution of Daniel and his friends. And chapter 5 ( C' ) should follow chapters 7 and 8 ( A" ). Instead, it is put in parallel with chapter 4 ( C ). In both divine judgements are pronounced against arrogant Babylonian kings.
Grouping Emphasizes Prophecies
This chiastic grouping of chapters having the same theme has important implications when it comes to the chapters containing prophecies ( A, A', A", A'" ). Not only are they parallel because they contain prophecies, but the prophecies themselves are parallel to each other. This parallelism between the prophecies has been recognized for millennia. This does not mean, however, that Christian commentators have identified the same kingdoms in each chapter. While chapters 2 and 7 have generally - though not exclusively[11] - been interpreted as extending to Roman times, chapter 8, for example, has traditionally been applied to the time of Antiochus Epiphanes.[12]
Historical accuracy
Dating to the 2nd century BCE; the Book of Daniel is the youngest text in the Hebrew Bible. Nevertheless, there has been some debate on the possibility that some of its content may be informed by historical events of the Achaemenid period. Thus, a major critic of Daniel, H. H. Rowley considered chapter 11 as "a first-class historical source for that period"[13] Another scholar ranked the fifth chapter of Daniel "just below the cuneiform literature", for accuracy as far as outstanding events are concerned, for non-Babylonian records on the close of the Neo-Babylonian Empire.[14]
Even allowing for such possible exceptions, most of the content of the narrative is unhistorical. The six objections given below represent, in order of significance, illustrates some of the major anachronisms.
Darius the Mede
Some historians criticize the notion of a separate Mede rule by pointing out that the Persians at that point in history had control over the Medes, and that the contemporary cuneiform documents, such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Babylonian Chronicle, leave no room for any Mede occupation of Babylon before the Persians under Cyrus conquered it. It has been suggested[15] that the author's apparent confusion on this issue could be due to his reliance on Jeremiah (see Dan. 9:2): and Jeremiah prophesied (in Jeremiah 51:11), at the height of the Median empire's power, that Babylon would fall to the Medes.
The personage whom Daniel describes as taking control of Babylon after Belshazzar is deposed is named as Darius the Mede, who rules over Babylon in chapters 6 and 9. Daniel reports that Darius was 'about 62 years old' when he was 'made king over Babylon.' Darius the Mede, while mentioned in the book of Daniel, the works of Flavius Josephus, and Jewish Midrash material, is not known from any primary historical sources. Neither the Babylonian nor the Persian histories record such a person. Herodotus, who wrote his history about 440 BCE, records that Babylon fell to the Persian army, under the control of King Cyrus, who had conquered the Median Empire as early as 550 BCE.
As Darius the Mede is unknown to any other source, many historians view his presence in Daniel as simply a mistake of a much later author, who has perhaps inadvertently placed the Persian King Darius I at an earlier date than he actually reigned.[16] Three key pieces of information seem to support this. Firstly, Darius I, like Cyrus, also conquered Babylon and personally commanded the Persian army that took the city in 522 BCE to put down a rebellion. Secondly, Daniel's reference to Darius organising the empire by appointing satraps and administrators fits Darius I perfectly: he is known to history as the Persian king par excellence who professionalised the empire's bureaucracy and organised it into satrapies and tax districts. Thirdly, Darius I was an important figure in Jewish history, remembered as a king associated with Cyrus who permitted the returned exiles to rebuild the temple (see Ezra chs 1-6).
In Daniel 9:1, Darius is said to be the son of Ahasuerus, commonly acknowledged to be a variant spelling of Xerxes (Esther 1:1). Darius I was the father of a king called Xerxes.[15]
Responses to the problem of Darius the Mede
As no ruler of this name is recorded, scholars have attempted to identify him with other figures:
- "Darius the Mede" as Cyrus the Great
This theory was first proposed by Donald Wiseman in 1957.[17] Unlike Gubaru or Astyages, Cyrus the Great of Persia was the king who took over the Babylonian Empire. Cyrus was also married to a Mede, and had a Median mother.[18] Indeed, his maternal grandfather Astyages, to whom he owed fealty, was the so-called "Last King of the Median Empire." An analysis of variant early texts, particularly the Septuagint, reveals that the names "Darius" (דריוש DRYWS in Hebrew) and "Cyrus" (כורש KWRS) are reversed in 11:1, and may have been miscopied elsewhere. The appellation "Mede" (Heb. מדי MDY) may have been used as an ethnic term to apply to Persians as well, who were of the same race.[19] In addition, Dan. 6:28, "So Daniel prospered during the reign of Darius and the reign of Cyrus the Persian", could also be translated, "So Daniel prospered during the reign of Darius, that is, the reign of Cyrus the Persian."[20] Furthermore, kings commonly took dual titles and Nabonidus, Cyrus' cousin, referred to Cyrus as "the king of the Medes."[18]
- "Darius the Mede" as Gubaru/Ugbaru
Gubaru was the governor of Gutium, who actually led Cyrus's army that captured Babylon in the month of Tashritu in the 17th year (see Pierre Briant below).[21] Two weeks later Cyrus made his triumphal entry into Babylon and a week after that Gubaru died. It is possible that Cyrus may have rewarded Gubaru with a regional governorship for capturing the capital of the Babylonian Empire and ending the war. Furthermore, under the first translation of Dan. 6:28, Darius ruled during the reign of Cyrus, and Dan. 5:31 states that Darius the Mede "received the kingdom" of the Chaldeans. Complicating this view is the question of whether or not Gubaru and Ugbaru are two different people, or simply variant spellings of the same name.
Verse 1 of "Bel and the Dragon" mentions Astyages the Mede, who was indeed the last king before Cyrus; but nearly the same verse is added in the Greek LXX after the end of chapter 6 of Daniel, but with "Darius" in place of "Astyages". ( LXX Dan. 14:1 and Dan 6:29)
- "Darius the Mede" as king of the Medes
Talmudic and midrashic sources describe Darius the Mede as the uncle and father-in-law of Cyrus the Great, to whom Cyrus owed fealty. After Darius's death, Cyrus took the throne. According to Josippon, the Ahasuerus in the book of Esther was the son of Darius the Mede. The Midrash Tanchuma describes the fall of Babylon as described in Daniel and adds to the narrative Darius taking Vashti, the daughter of Belshazzar, as a wife for his son Ahasuerus.
- "Darius the Mede" as Cyaxares II
The little we know of Cyaxares from extra-Biblical sources matches the description offered in the Book of Daniel. According to Daniel, he began ruling when he was 62 years old (chapter 5, verse 31), appointed 120 satraps to govern over their provinces or districts (chapter 6, verse 1), was made king over the realm of the Chaldeans (chapter 9, verse 1), and pre-dated Cyrus (chapter 11, verse 1).
Belshazzar
For many years Belshazzar (Akk. bêl-šar-usur), was an enigma for historians. The book of Daniel states that he was "king" (Ar. מֶלֶך) the night that Babylon fell (chap. 5) and says that his "father" (Ar. אַב) was Nebuchadnezzar (5:2, 11, 13, 18). Prior to 1854, archeologists and historians knew nothing of Belshazzar outside the book of Daniel. Indeed, while the deuterocanonical Book of Baruch (Baruch 1:11, 12) and the writings of Josephus (Antiquities 10.11.2-4 §231-247) do mention Belshazzar, the references to Belshazzar in these works are ultimately dependent on the book of Daniel.[22] Both Xenophon (Cyropaedia, 7.5.28-30[23]) and Herodotus (The Histories, 1.191) recount the fall of Babylon to Cyrus the Great, yet neither of these writers give the name of the king of Babylon. Additionally, both Berossus’ and Ptolemy's king lists have Nabonidus (Akk. Nabû-nā'id) as the last king of Babylon with no mention of Belshazzar.
From that time new evidence from Babylon has verified the existence of Belshazzar as well as his co-regency during the absence of his father, Nabonidus, in Temâ. For example, In the Nabonidus Cylinder, Nabonidus petitions the god Sin as follows: "And as for Belshazzar my firstborn son, my own child, let the fear of your great divinity be in his heart, and may he commit no sin; may he enjoy happiness in life". In addition, The Verse Account of Nabonidus (British Museum tablet 38299) states, "[Nabonidus] entrusted the army (?) to his oldest son, his first born, the troops in the country he ordered under his command. He let everything go, entrusted the kingship (Akk. šarrûtu) to him, and, himself, he started out for a long journey. The military forces of Akkad marching with him, he turned to Temâ deep in the west" (Col. II, lines 18 - 29. 18). In line with the statement that Nabonidus "entrusted the kingship" to Belshazzar in his absence, there is evidence that Belshazzar's name was used with his father's in oath formulas, that he was able to pass edicts, lease farmlands, and receive the "royal privilege" to eat the food offered to the gods.
The available information concerning Belshazzar's regency goes silent after Nabonidus' fourteenth year. According to the Nabonidus Chronicle, Nabonidus was back from Temâ by his seventeenth year and celebrated the New Year's Festival (Akk. Akitu). Whether or not Belshazzar continued his regency under his father's authority after his return cannot be demonstrated from the available documents. Some scholars have argued that the non-observance of the Akitu during Nabonidus' absence demonstrates that Belshazzar was not the "king" since it shows that he could not officiate over the festival. However, The Verse Account of Nabonidus says, "Nabonidus said: 'I shall build a temple for him (the Moon god Sin)...till I have achieved this, till I have obtained what is my desire, I shall omit all festivals, I shall order even the New Year's festival to cease!'" Thus, the halting of the Akitu may have been done by the king's command rather an inability on the part of Belshazzar. This stated, the fact that Belshazzar did not disobey his father's command is evidence that Nabonidus remained the official (and actual) king of Babylon.

There is no evidence that Belshazzar ever officially held the title of "king" as he is never called such in the Nabonidus Cylinder. Furthermore, the Aramaic term מלך (mlk, king) applied in Daniel could be used to translate titles of various levels of high ranking officials. (This can be seen in the case of a 9th century BCE Akkadian/Aramaic bilingual inscription found at Tel Fekheriyeh in 1979 which reads "king" for the Akkadian "governor".) A contract tablet dating to the third year of his regency (550 BCE) includes the designation "son of the king."[24] This, of course, is not proof that he possessed any status as the official king of Babylon. The bottom line is that Nabonidus was still alive when Cyrus conquered Babylon, and had not been replaced as the official king of Babylon by Belshazzar.
No known extrabiblical text indicates a blood relation between Nebuchadnezzar and Belshazzar. Historians have objected to this aspect of the record in Daniel. There were several rulers over Babylon between the death of Nebuchadnezzar and the rulership of Nabonidus and Belshazzar. Some have attributed the lack of mention of these rulers as indicating the author mistakenly thought that the two rulerships were consecutive. The Jewish Encyclopedia, holding to a later date of the book (see 'Date'), supposed that "during the long period of oral tradition the unimportant kings of Babylon might easily have been forgotten, and the last king, who was vanquished by Cyrus, would have been taken as the successor of the well-known Nebuchadnezzar." Based on this reasoning, some historians have considered the reference to Belshazzar's relationship to Nebuchadnezzar simply an error based on the above misconception.
However, there is another explanation. Belshazzar is never called an independent king in the book of Daniel.[25] In fact, in Daniel 5:7, 16, 29 Belshazzar implies that he is the second ruler in the kingdom, not the sole ruler; and yet, he has sufficient power to make someone the third ruler in the kingdom. Secondly, co-regencies were not that uncommon in the Ancient Near East.[26][27] Third, Wilson, in the previous reference, showed that the very word "king" was used in a variety of ways other than that which we use today. The same also applies to the use of the word "son"--it doesn't necessarily mean a biological relationship and can carry the meaning "successor." For example, the 9th Century Assyrian Black Obelisk lists Jehu as the "son of Omri" even though Jehu was from a different lineage and did not take the crown directly after Omri.[18] Finally, Daniel is not writing an official state document for Babylon such as one would expect from the court scribes, although the lack of accurate specificity in the references also tends to be inconsistent with the claim of an early date for Daniel.[28][29]
Madness of Nebuchadnezzar
There are also historical objections to the account of the insanity suffered by Nebuchadnezzar found in the fourth chapter of Daniel. Three Aramaic Dead Sea Scrolls fragments known as The Prayer of Nabonidus (4QPrNab, sometimes given as 4QOrNab) seem to contain a number of parallels with Daniel chapter four: a Babylonian king (spelled N-b-n-y) is afflicted by God with an "evil disease" for period of seven years; he is cured and his sins forgiven after the intervention of a Jewish exile who is described as a "diviner"; he issues a written proclamation in praise of the Most High God, and speaks in the first person. These tiny fragments turned up in a collection of Dead Sea Scrolls possessed by the Jordanian Government, and were first published by Milik in 1956. Long before this, scholars had speculated that Nabonidus' exile in Teima lay behind the story of Nebuchadnezzar's banishment and madness in Daniel chapter four. [30]
There are also a number of differences between The Prayer of Nabonidus and the account of Nebuchanezzar's madness:
- Different kings are involved in the two accounts
- Nebuchadnezzar's "affliction" was of the mind whereas Nabonidus' seems to have been a skin disease.
- According to one possible translation, the exorcist or diviner heals Nabonidus and pardons his sins, whereas in Daniel Nebuchadnezzar is cured when he "[lifts] up [his] eyes to heaven" and "[acknowledges] that the Most High is soverign". (An alternative reading with sound support, however, attributes the healing and forgiveness of Nabonidus' sins to God [31] )
- Nebuchadnezzar's illness occurs in Babylon; Nabonidus is stricken in Tema. (The end result, though, is that both kings are absent from Babylon for the duration of their illnesses, since Nebuchadnezzar is "driven away from mankind." (4:33, NASB))
- Finally, some of the words and phrases of the prayer have to be inferred from the context because the text is fragmentary. [Archer, Gleason L. "Daniel", Expositor's. Vol. 7 (Zondervan, 1985): 15; he cites Harrison, R. K. Introduction to the Old Testament. (Tyndale, 1969): 1118-9]
Some feel that the Prayer of Nabonidus shows signs of dependence upon the book of Daniel,[32][33] while others agrue for direct dependence in the reverse direction. Regardless of whether there is any direct literary dependence, however, the "general consensus" of scholars is that Daniel four ultimately draws upon traditions and legends about Nabonidus.[34]
Matthias Henze further suggests that the story of Nebuchadnezzar's madness draws on the Mesopotamian epic of Gilgamesh. He argues that the author of Daniel uses elements from the description of the wild man Enkidu, who roams the steppe with the animals, to paint a sarcastic and mocking portrait of the king of Babylon.[35]
It is possible that a reference to the insanity of Nebuchadnezzar is to be found in a cuneiform text: BM 34113.[36][37]
Date of Nebuchadnezzar's first siege of Jerusalem
The Book of Daniel begins by stating:
- In the third year of the reign of Jehoi'akim king of Judah came Nebuchadnez'zar king of Babylon unto Jerusalem, and besieged it. And the Lord gave Jehoi'akim king of Judah into his hand, with part of the vessels of the house of God: which he carried into the land of Shinar to the house of his god; and he brought the vessels into the treasure house of his god. (King James Version)
This appears to be a description of the first siege of Jerusalem in 597 BCE, which occurred in the 11th year of Jehoiakim and into the reign of his son Jehoiachin. (see (2Kings 24), (Daniel 5:1-5), and (2Chronicles 36)). The third year of Jehoiakim (606 BCE), saw Nebuchadnezzar not yet King of Babylon, and the Egyptians still dominant in the region. Nebuchadnezzar did not become "King of Babylon" until after the Battle of Carchemish, in Jehoiakim's fourth year(Jer 25:1). In Jeremiah 36:9, we find Jehoiakim in Jerusalem in his fifth year, two years after the time that Daniel claims he was carried away to Babylon.
The Babylonian Chronicle records that Nebuchadnezzar first defeated the Egyptians under Pharaoh Necho in Battle of Carchemish. He then conquered the whole of Hatti-land, a region that includes the kingdom of Judah. Apologists argue this would coincide with the coming of Nebuchadnezzar recorded in Dan 1:1. The historian Berossus records that Nebuchadnezzar took Jewish captives back to Babylon after the Battle of Carchemish.[38] The Berossus account however is based on the mistaken premise that Babylonia already ruled Syria, Israel and Egypt before the Battle of Carchemish. The Berrosus excerpts are very fragmented and may not have been preserved unadulterated.[39]
Hananiah, Mishael, and Azariah
Dan. 1:6-7 records that Daniel was accompanied in the courts by three other Jews: Hananiah, Mishael, and Azariah. The chief officials gave them new Babylonian names: Shadrach, Meshach, and Abednego, respectively. In Dan. 3:8-23, these same three persons refuse to perform an act of worship before an image of Nebuchadnezzar, which results in their subjection to the death penalty by burning. However, according to Dan. 3:24-30, God delivers them from the fiery furnace.
Seventh Day Adventist Professor William Shea (1982) refers to a clay prism that was found in Babylon with five columns of text listing various officials of the government. Three of the officials are listed as "Mushallim-Marduk, [one of] the overseers (lit.:heads) of the slave-girls", "Ardi-Nabu, the sipiru-official of the crown prince", and "Hanunu - chief of the royal merchants",[40] and Dan. 2:49 states, "Moreover, at Daniel's request the king appointed Shadrach, Meshach and Abednego administrators over the province of Babylon, while Daniel himself remained at the royal court." Some conservative Christian writers have therefore connected Hanunu with Hananiah, Mushallim-Marduk with Meshach, and Ardi-Nabu with Abednego; however, it is unclear why Hananiah would be referenced by his Hebrew name (Oppenheim (see citation) posits that "Hanunu" is "Phoenician" rather than Hebrew) and not his Babylonian one, Shadrach. There is no other evidence to connect these figures with the ones mentioned in the Book of Daniel.
Four Persian Kings
In Daniel 11:2-4, the angel Gabriel informs the prophet of four Persian kings before the coming of Alexander the Great.
- And now will I shew thee the truth. Behold, there shall stand up yet three kings in Persia; and the fourth shall be far richer than they all: and by his strength through his riches he shall stir up all against the realm of Grecia. And a mighty king shall stand up, that shall rule with great dominion, and do according to his will. And when he shall stand up, his kingdom shall be broken, and shall be divided toward the four winds of heaven.
Since the author of Daniel wrote during the reign of Cyrus (Daniel 10:1), the first three kings are Cambryses, Smerdis, and Darius I. The fourth king is Xerxes I of Persia who is renowned for his attack on Greece in the Greco-Persian Wars. Strictly speaking the history is inaccurate, although the following survey of seleucid and ptolemaic kings in chapter eleven also contains gaps as the writer focuses on key events rather than a complete history of the period.
The kings from Cyrus to Alexander are:
- Cyrus (549 - 530 BCE)
- Cambyses (530 - 522 BCE)
- Smerdis (522 BCE)
- Darius I (522 - 486 BCE)
- Xerxes (485 - 465 BCE)
- Artaxerxes I (465 - 424 BCE)
- Xerxes II
- Sogdianus
- Darius II (423 - 404 BCE)
- Artaxerxes II (404 - 358 BCE)
- Artaxerxes III (358 - 338 BCE)
- Artaxerxes IV Arses (338 - 336 BCE)
- Darius III (336 - 330 BCE)
Dating and content
Scholarly view
Modern critical biblical scholarship dates the Book of Daniel to the second century BCE,[2][3] There is general agreement among scholars that Daniel's revelations are actually vaticinia ex eventu or prophecies after the event.[41] and the traditionalist view which dates it to the 6th century has been rejected by the scholarly community since the end of the nineteenth century.[34][42][43][44][45][46][47] In the Roman Catholic community it has been the norm since World War II.[34] Evangelical Old Testament scholar John Goldingay argues that many of the prophecies in Daniel, in particular the prophecies of Daniel 11, were written after the fact (ex eventu). But, says Goldingay, this was not a deceptive ploy, or a "pious fraud" (Porphyry of Tyros). Rather, the author/redactor of Daniel was employing a then common literary genre, which Goldingay describes as "quasi-prophecy", and so the author's original readers would have recognized this genre and therefore not been led to believe that the quasi-prophecies were actual prophecies (one might add that the readers would have doubtless known that the piece of literature being read to them had just been written, i.e. had been written in the 2nd century; or put differently, they would have realized that the piece of literature had not been written in the 6th century).[48]
Antiochus IV Epiphanes desecrated and looted the Jerusalem Temple around 167 BCE, outlawed the Jewish religion, massacred observant Jews and precipitated a national crisis that is commemorated to this day in the Feast of Hanukkah (which recalls the rededication of the temple). The Book of Daniel (in its final form) is written, according to the mainstream view, in response to that crisis. Even when the fourth kingdom of chapters two and seven began to be reapplied to Rome in pre-Christian and early Christian times the memory of Antiochus was still vivid. This is evidenced by the fact that leading Jewish and patristic commentators such as Josephus, Hippolytus, and Jerome continued to apply sections of Daniel (especially chapter 8) to the activities of Antiochus.
Traditionalists, making a case for an earlier date for the Book of Daniel, make reference to Josephus, who states that upon Alexander the Great's approach, a small party met him outside of Jerusalem with a copy of the book of Daniel, telling him that his presence was ordained by scripture. However, most scholars agree that this story is not true.[49][50][51] Harvard scholar Shaye J. D. Cohen denies the historicity of Alexander's visit to Jerusalem and suggests that the Alexander story is a combination of several sources.[52] Additionally, some point to the Dead Sea scrolls found at Qumran dating from the mid-2nd century BCE to 70 CE. These scrolls include eight manuscripts of Daniel dating from about 125 BCE(4QDanc) to about 50 CE(4QDanb).[2] The premise is that there must have been much time between the original writing and the copying of the manuscripts found at Qumran, since it would have taken time for the book to have gained acceptance and be made available for copying.[53] Of significance is the fact that the Book of Daniel was never grouped with the Hebrew Nevi'im (the Prophets) but has always belonged to the Ketuvim (the writings). Bryan Rennie argues that if the author had been accepted to be a sixth century Jew of the Exile his work would have pre-dated Ezra and Nehemiah and would have been considered authoritative enough to group it with the other prophets. [54]
In addition, the canon of the Prophets (Nevi'im) was closed by about 200 BCE with the composition of Malachi.[55] The apocryphal book of Sirach, written about 180 BCE, contains a long section (chapters 44-50) in praise of "famous men" from Jewish history that does not include Daniel. However I Maccabees, composed about 100 BCE, repeats much of that list with the addition of Daniel and the three youths in the fiery furnace, leading to the conclusion that these stories were likely added to Hebrew literature sometime after 180 BCE.[56]
The traditionalist view holds that the work was written by a prophet named Daniel who lived during the sixth century BCE since Ezekiel who lived at that time mentions Daniel three times (Ezekiel 14:14, 20; 28:3). The Hebrew spelling in Ezekiel however suggests "Danel" is more correct.[57] Though in the words of Albright, the 'name Danilu, Danel is well attested (in different writings and perhaps with different meanings attributed to it) in Old Assyrian, Old Babylonian, Northwest Semitic . . .' and that 'Danil is the Babylonian pronunciation of non-Accadkian Semitic Dan'il, "Daniel" . . .'[58] (see also Danel and the Danel of Ezekiel). According to the Encyclopædia Britannica article on the Septuagint: "Analysis of the language has established that the Torah, or Pentateuch (the first five books of the Old Testament), was translated near the middle of the 3rd century BCE and that the rest of the Old Testament was translated in the 2nd century BCE."[59]
Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Critical scholars have asserted that the prophecies in the Book of Daniel reflect the persecutions of the Jews by the Greek Seleucid king Antiochus IV Epiphanes who ruled the Jews from 175–164 BCE, and his desecration of the altar in the temple at Jerusalem, and consequently they date its composition to that period. In particular, the vision in Chapter 11, which focuses on a series of wars between the "King of the North" and the "King of the South", is generally interpreted as a record of Levantine history from the time of Alexander the Great down to the era of Antiochus IV, with the "Kings of the North" being the Seleucid kings of Syria and the "Kings of the South" being the Ptolemaic rulers of Egypt.
Scottish theologian John Drane notes that other details of the stories in the early chapters of Daniel are also similar to the prevailing conditions in the era of Antiochus. "Belshazzar for example, falls from power because he defiled the sacred objects taken from the Temple in Jerusalem (Dan. 5:1-4), in much the same way as Antiochus repeatedly robbed the Temple in Jerusalem. The worship of the great statue set up by Nebuchadnezzar (Dan. 3:1-18) and the story of the Bel found in the Septuagint highlighted the same issues as Antiochus' action in setting up an image of Zeus in the Temple at Jerusalem. Indeed it may be implied that the images were actual statues of the kings themselves. Even the story of Nebuchadnezzar's madness (Dan. 4:19-33) may have been intended to be reminiscent of the commonly held belief that Antiochus was mad ("epimanes"). The people of a later age would also recognize those apostate Jews who collaborated with the unbelieving Seleucids in the duplicitous figures of the spies and informers who plotted against Daniel and ensured that he was shut up in the den of lions (Dan. 6:1-14). The issue of food, which features so largely in the opening story of Daniel (Dan. 1:3-16), was one of the whole crucial points in the whole argument about Hellenism. Much of the opposition that sparked the Maccabean revolt was concerned with the unwillingness of faithful Jews to eat pork and other unclean foods".[60] Even the name Nebuchadnezzar contains a veiled reference to Antiochus Epiphanes to those acquainted with Hebrew numerology. In Hebrew, as in many other ancient languages, names and words often have numerical value (see Gematria). Nebuchadnezzar's name in cuneiform is Nabû-kudurri-uṣur which should be transliterated into Hebrew as נבוכדנאצר or Nebuwkadne'tstsar (as it is in Jer. 46:2, 39:11). It is unlikely to be a coincidence that when the numbers represented by "Nebuwkadne'tstsar" are added up, they come exactly the same figure (423) as the numbers of the name "Antiochus Epiphanes".[54][61]
This conclusion regarding the date of composition was first drawn by the philosopher Porphyry of Tyros, a third century pagan and Neoplatonist, whose fifteen-volume work Against the Christians is only known to us through Jerome's reply. The identification of Antiochus Epiphanes in Daniel, however, is a much older[62] interpretation which seems to be reflected, for example, in 1 Maccabees 1:54 (c100 BCE), where an idol of Zeus set up upon the altar of burnt offering under Antiochus is referred to as an "abomination of desolation" (cf. Dan. 9:27, 11:31).[63] This identification is made explicit in Josephus' exposition of Daniel chapter eight (Antiquities 10:11, c94 AD) where he almost certainly cites a common Jewish interpretative tradition by identifying the "little horn" as Antiochus. According to British historian Bryan Rennie, the conclusion that the Book of Daniel was written at the time of the profanation of the Temple by Antiochus IV would explain why the author is not very precise about sixth century events, why he is so precise about the time of Antiochus, and why he was never counted among the prophets.[54] Scholars are virtually unanimous in regarding the Book of Daniel as a message of encouragement to those people(hasidim)[64] suffering for their faith under the oppression of Antiochus IV Epiphanes.
Four Kingdoms
Most biblical scholars have concluded that the four kingdoms beginning with Nebuchadnezzar, mentioned in the "statue vision" of chapter 2, are identical to the four "end-time" kingdoms of the vision in chapter 7, and consider them to represent (1) Babylonia, (2) Media, (3) Persia, and (4) Greece.[65][66][67] There is a literary tradition through various cultures which saw history pass through four kingdoms. These four kingdoms were Assyria, Media, Persia and Macedonia as part of Greece.[68] As Daniel was set after the time of the Assyrians, Babylon was more relevant to the literary structure.
| Chapter | Parallel sequence of events and its interpretation as understood by scholars | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daniel 2 | Gold Head identified as Nebuchadnezzar and his kingdom in v. 36-39 i.e. Babylon |
Silver Breast and arms kingdom of Media |
Bronze Belly and thighs kingdom of Persia |
Iron Legs kingdom of Greece |
Feet and toes partly of iron and partly of baked clay Syria (Seleucids) and Egypt (Ptolemies) |
Kingdom of God | End | |
| Daniel 7 | Winged Lion Babylon |
Bear Media |
4 headed leopard Persia |
Terrible beast with iron teeth Greece |
10 horns 10 kings of the Seleucid Dynasty |
Little horn Seleucid king Antiochus IV Epiphanes |
Kingdom of God handed over to the people (Jews) of the Most High | End |
| Daniel 8 | Two-horned Ram identified as the kings of Media and Persia in v.20 |
Unihorn Goat identified as the king of Greece in v.21 large horn is Alexander the Great |
4 horns Macedonia, Pergamon, Egypt (Ptolemies) and Syria (Seleucid Dynasty) |
Little horn Seleucid king Antiochus IV Epiphanes |
End | |||
| Daniel 11 | Media | 4 kings of Persia | Greece | kings of the north and south king of the north is Syria (Seleucid Dynasty), king of the south is Egypt (Ptolemies) |
Contemptible Person Seleucid king Antiochus IV Epiphanes |
Deliverance of Jews | End | |
To a modern reader the relationship between the Medes and the Persians is not transparent in Daniel.
- In Dan. 5:28, we are told that Babylon would be divided and given to the Medes and Persians, apparently indicating that the two kingdoms existed separately at the same time, though historically when the kingdom of the Medes was in power, the Persians were vassals until they reversed the situation.
- Three times we read about "the law of the Medes and the Persians", (Dan. 6:8, 12, and 15). Though the Medes and the Persians were Iranian peoples and so shared a cultural heritage, one reading of "the law of the Medes and the Persians" suggests that the phrase indicates the two groups must have merged.
- Dan. 8:3 features a ram with two horns, with the Medes being represented by the first horn to arrive and the Persians by the longer second horn. These two horns are the kings of the Media and Persia(Dan. 8:20). When the Babylonian kingdom falls (Dan. 5:30-31), the new ruler is called Darius the Mede(Dan. 9:1). He is followed by Cyrus, king of Persia(Dan. 10:1). Darius the Mede is unknown in secular history. The Median kingdom had already been conquered by Cyrus the Persian, and it was Cyrus who captured Babylon.[69][70] As noted previously, however, a late author's apparent reliance on Jeremiah may explain this (Dan. 9:2, Jer. 51:11, 51:28-30).
- Finally Daniel 10 talks solely about Persia. Cyrus is the king of Persia (Dan. 10:1). The prince (=angel) of the kingdom of Persia struggles with Michael (Dan. 10:13). Daniel is told that after the prince of Persia, the prince of Greece will come(Dan. 10:20).
Although Daniel shows no interest in the ancestry of Cyrus, it has been pointed out that Cyrus was married to a Mede and himself had Median blood. This some have thought would make the Medes and Persians merged kingdoms by marriage at the time of the conquest of Babylon. However, Persian inscriptions from the time of Darius I show Media as a subordinate kingdom which paid tribute to Persia.
- Protestant historicist interpretation
Some Historicist Christians (e.g. Young, Smith, Anderson, etc.) believe that the first four should be identified as (1) the Neo-Babylonian empire, (2) the Medo-Persian empire (3) the Macedonian empire of Alexander and his successors, and (4) the Roman empire. Parallel elements of each prophecy are the same color.
| Chapter | Parallel sequence of prophetic elements as understood by Historicists[71][72] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Past | We are here | The Future | ||||
| Daniel 2 | Head Gold (Babylon) |
Chest & 2 arms Silver |
Belly and thighs Bronze |
2 Legs Iron |
2 Feet with toes Clay & Iron |
Rock God's unending kingdom left to no other people |
| Daniel 7 | Winged Lion | Lopsided Bear | 4 Headed/4 Winged Leopard |
Iron toothed beast w/Little Horn |
Judgment scene Beast slain |
A son of man comes in clouds Given everlasting dominion He gives it to the saints.[73] |
| Daniel 8 | 2-horned Ram (Media-Persia) |
Uni- / 4-horned Goat 4 Winds (Greece) |
Little Horn A Master of Intrigue |
Cleansing of Sanctuary Leads to: |
(Kingdom of God) | |
| Daniel 11-12 | Kings (Persia) |
North & South Kings 4 Winds (Greece) |
North & South Kings A Contemptible Person of Intrigue Pagan & Papal Rome |
North & South Kings End Times Global religio-political Government |
Michael stands up Many dead awake To everlasting life |
|
(Nations in parentheses are interpretation of symbols as given in the text. Nations in small italics are Historicist interpretation. "One like a son of man" and "Michael" are understood to be the same being.)
- Other views
Others (e.g. Stuart, Lagrange) have advocated the following schema: (1) the Neo-Babylonian, (2) the Medo-Persian, (3) the short-lived rule of Alexander, and (4) the rival Diadochi, viz. Egypt and Syria.[74]
Language
Scholars have speculated about the bilingual literary structure of Daniel - Chapters 2 through 7 in Aramaic, the rest in Hebrew. One of the most frequent speculations is that the entire book (excepting 9:4-20) was originally written in Aramaic, with portions translated into Hebrew, possibly to increase acceptance[75] - many Aramaisms in the Hebrew text find proposed explanation by the hypothesis of an inexact initial translation into Hebrew.
According to John Collins in his 1993 commentary, Daniel, Hermeneia Commentary, the Aramaic in Daniel is of a later form than that used in the Samaria correspondence, but slightly earlier than the form used in the Dead Sea Scrolls, meaning that the Aramaic chapters 2-6 may have been written earlier in the Hellenistic period than the rest of the book, with the vision in chapter 7 being the only Aramaic portion dating to the time of Antiochus. The Hebrew portion is, for all intents and purposes, identical to that found in the Dead Sea Scrolls, meaning chapters 1 and 8-12 were in existence before the late 2nd century BC.[76][77]
Contrary to the above, the Expositor's Bible Commentary (Zondervan, 1990) claims that the language of Daniel, in comparison with the Hebrew and Aramaic texts of the Hellenistic period, "prove quite conclusively to any scholar that the second-century date and Palestinian provenance of the Book of Daniel cannot be upheld any longer without violence being done to the science of linguistics." It adds that the serious mistakes of the Septuagint to render many Persian and Accadian terms, as the offices mentioned in Dan. 3:3, proves ignorance of words of the old past, already forgotten in the Hellenistic period, indicating that the Book of Daniel was written in the late 6th century BCE.[78]
E.C. Lucas is more cautious in his assessment of linguistic arguments as well. Evaluating Collins' approach, he considers "the wide geographical spread from which the material comes and the implicit assumption that linguistic developments would have occurred uniformly throughout this area" a weakness and concludes, "The character of the Hebrew and Aramaic could support a date in the fifth or fourth century for the extant written form of the book, but does not demand a second-century date." He agrees with Collins that there are "clear differences" between Qumran Hebrew and the Hebrew of Daniel.[79]
Loan words
Three Greek words used within the text have long been considered evidence for a late dating of Daniel. All three are terms for musical instruments, κιθαρις (cithara), ψαλτηριον (psaltery) and συμφωνια (symphonia). The existence of the Greek word symphonia was cited by Rowlings as having its earliest known use in second century BCE, but it has subsequently been shown that Pythagoras born in the sixth century BCE used the term.[80][81] while its adjectival use meaning "in unison" is found in the 'Hymni Homerica, ad Mercurium 51'; both instances date from the sixth century BCE, the supposed setting of Daniel.
It is known that "Greek mercenaries and slaves served in the Babylonian and Assyrian periods, some of whom were undoubtedly versed in Greek music and musical instruments." It has been speculated that this would explain the existence of the three Greek musical terms in Daniel's book. On the other hand, it has been claimed that the non-existence of other Greek words is a strong witness against the theory of the writing of the book in the Hellenistic period, since "it is inconceivable that Greek terms for government and administration would not have been adopted into Aramaic by the second century BCE"[82] Even John Goldingay, a proponent of the late date, admits "the Greek words hardly necessitate a very late date." [83]
There are also nineteen Persian loan-words in the book, most of them having to do with governmental positions. Judea was under Persian administration for two centuries until the arrival of Alexander the Great in 333 BC.
Use of the word 'Chaldeans'
The book of Daniel uses the term "Chaldean" to refer both to an ethnic group, and to astrologers in general. According to Montgomery and Hammer Daniel's use of the word 'Chaldean' to refer to astrologers in general is an anachronism, as during the Neo-Babylonian and early Persian periods (when Daniel is said to have lived), it referred only to an ethnicity. (Compare the later Chaldean Oracles).
Textual witness
A total of eight copies of the book of Daniel have been found amongst the Dead Sea Scrolls.[84] All eight manuscripts have been dated within the space of 175 years ranging from about 125 BCE (4QDanc) to about 50 AD (4QDanb).[2] There were at least three versions extant: the twelve-chapter version preserved in the Masoretic text and the two longer Greek versions, the Theodotion version (ca. 2nd cent. AD) and the original Septuagint version ( ca. 100 BCE; see above sections).[85] Both Greek versions contain the apocryphal chapters (ca. 100 BCE) not found in the Hebrew/Aramaic text of Daniel. Theodotion's translaton is much closer to the Hebrew/Aramaic Daniel of the Masoretic Hebrew Bible, and became so popular that it replaced the original Septuagint version of Daniel in all but two manuscripts of the Septuagint itself.[86][87][88] For its part, the older (pre-Theodotion) Septuagint edition sometimes agrees more with the older Hebrew / Aramaic readings of the text of the Qumran fragments, against the more recent Theodotion / Masoretic version reflected in modern translations.
Unity of Daniel
Whereas many scholars conclude a second century dating of the book in its final form,[89] scholarship varies greatly regarding the unity of Daniel. Many scholars, finding portions of the book dealing with themes they do not believe fit with the time of Antiochus, conclude separate authors for different portions of the book. Included in this group are Barton, L. Berthold, Collins, and H. L. Ginsberg. Some historians who support that the book was a unified whole include J.A. Montgomery, S.R. Driver, R. H. Pfeiffer, and H.H. Rowley in the latter's aptly titled essay "The Unity of the Book of Daniel" (1952). Those who hold to a unified Daniel claim that their opponents fail to find any consensus in their various theories of where divisions exist. Montgomery is particularly harsh to his colleagues, stating that the proliferation of theories without agreement showed a "bankruptcy of criticism." They also charge that composite theories fail to account for the consistent thematic portrayal of Daniel's life throughout the Book.
Christian uses of Daniel
| Christian Eschatology | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eschatology views | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
As mentioned above, the prayer of Azariah and the Song of the Three Children from the deuterocanonical parts of Daniel are widely used in Orthodox and Catholic prayer.
The various episodes in the first half of the book are used by Christians as moral stories, and are often believed to foreshadow events in the gospels.
The apocalyptic section is important to Christians for the image of the "one like a son of Man"(Dan. 7:13),[90] and Jesus is presented using the same wording in the book of Revelation in 1:13-15.[91] The connection with Daniel's vision (as opposed to the usage in the Book of Ezekiel) is made explicit in the Gospels of Matthew and Mark (Matt. 26:64; Mark 14:62).[92] According to the gospels, Jesus used the title "Son of Man" as his preferred name for himself (Matt. 26:64; Mark 14:62). Christians sometimes see this as a claim by Jesus that he is the Messiah. According to the New American Bible and some Christian theologians, "one like a son of man" represents "the saints of the Most High" as interpreted in the vision later(Dan 7:16-18, 21-22, 25-27) and Jesus made the title "Son of Man" a distinguishing self reference.[93][94][95] Later Jewish interpreters interpreted this figure as the Jewish Messiah. Such interpretation appears in the Similitudes of Enoch and 4 Ezra.[96][97]
Traditional Christians have embraced the prophecies of Daniel, as they believe they were clearly advised by their Messiah, Jesus Christ of Nazareth, to be watchful for their fulfillment in the "End Times" of this world. In the Olivet discourse (Mark 13:14, Matt. 24:15) Jesus himself is quoted as applying Daniel's prophecy of a desolating sacrilege set up in the temple (Dan. 9:27, 11:31) to a future event — the AD 70 destruction of Jerusalem.[98][99] This would involve the leveling of the temple, flight from Judea, and would happen in Jesus' own generation (Mark 13: 2-4, 14, 30). Many Christians today re-apply this prediction to a final tribulation immediately preceding Judgement Day. Some consider the Prophecy of Seventy Weeks to be particularly compelling due to what they interpret to be prophetic accuracy.
According to some scholars, Dan. 12:2 is the earliest clear reference in the Old Testament to the resurrection of the dead,[100] with many of "your countrymen" awakening from death, some to eternal life and some to eternal disgrace. This belief is also expressed in 2 Maccabees and as in Daniel, is linked with the idea of divine retribution.[101] 2 Macc. 7:14 : And when he was now ready to die, he spoke thus: It is better, being put to death by men, to look for hope from God, to be raised up again by him; for, as to thee(Antiochus Epiphanes), thou shalt have no resurrection unto life. The notion of resurrection was to be elaborated in the New Testament and Christian doctrine.
The importance of Daniel's visions
Daniel's alleged presence in the royal court would have exposed him to the running of an empire. His knowledge, as in the case of other prophets, served as the basis for his revelations. Daniel's importance is that of introducing the age of the Gentiles, the framework for events from then to the last days.
Due to its apocalyptic character and its place in both the Jewish and Christian canons, the book of Daniel has had great influence in Jewish and Christian history.
Daniel was considered a prophet in the Qumran library (4Q174 aka 4QFlorilegium), and later by Josephus (Antiquity of the Jews 10.11.7 §266); the Book of Daniel was grouped among the prophets in the Septuagint (the Jewish Greek Old Testament), and by Christians. As far as known, however, Daniel has never been numbered with the prophets (or Nevi'im) in the Hebrew Bible (or Tanakh), but rather belongs to the section known as the Ketuvim (Hagiographa, or "Writings").
The Jewish exegete Rabbi Moses Ben Maimon, sometimes called simply RaMBaM and later called Maimonides, was so concerned that the "untutored populace would be led astray" if they attempted to calculate the timing of the Messiah that it was decreed that "Cursed be those who predict the end times." This curse can be both found in his letter Igeret Teiman and in his booklet The Statutes and Wars of the Messiah-King.
Rabbi Judah Loew ben Bezalel lamented that the times for the fulfillment of the prophecy of Daniel "were over long ago" (Sanhedrin 98b, 97a).
Many Orthodox Jews believe that the prophecy refers to the destruction of the Second Temple by the Romans in 70 AD. Secular scholars and some Evangelical scholars however, believe that the prophecy better fits the reign of Antiochus, and that it is an example of vaticinium ex eventu (prophecy after the fact).
Medieval study of angels was also affected by this book, as it is the only Old Testament source for the names of any of the angels, Gabriel and Michael (Dan 9:21; 12:1). The only other angel given a name is Raphael, mentioned in the deuterocanonical Book of Tobit.
Traditional tomb sites of Daniel
There are six different locations all claimed to be the site of the tomb: Babylon, Kirkuk and Muqdadiyah in Iraq, Susa and Malamir in Iran, and Samarkand in Uzbekistan.
See also
- Daniel 2 - Image prophecy
- Daniel 3 - Fiery furnace
- Daniel 5 - The writing on the wall
- Daniel 7 - Prophecy of the beasts
- Daniel 8 - Prophecy of goat/ram/horn
- Daniel 9 - Seventy-week prophecy
- Daniel 11 - Prophecy of Kings
- Additions to Daniel
- Bel and the Dragon
- Susanna (Book of Daniel)
- Antiochus Epiphanes
- Daniel Prophecy Literary Parallels
- Christian eschatology
- List of apocalyptic literature
- Book of Revelation
- Danel - Ugaritic hero identified with Daniel in Ezekiel (Ezek. 14:14-20)(Ezek. 28:3)
- Old English poem Daniel
- Siege of Jerusalem (70)
- Theodotion
- Greek Apocalypse of Daniel
Notes
- ↑ Elwell, Walter A.; Comfort, Philip W., eds (2008). Tyndale Bible Dictionary. Tyndale House Publishers, Inc.. p. 350. ISBN 1414319452. "Uncertainty about the authorship of the book of Daniel contributes to uncertainty about the date of its writing. If Daniel was the author of the whole book, a date in the second half of the sixth century BCE is likely. If he was not the author, a later date is possible. The conservative position has usually been that the book was written in the sixth century BCE. An alternative position is that it was written about 165 BCE. Evidence exists to support both the early and late dates of Daniel..."
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 VanderKam & Flint 2004, p. 137
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Apocalypticism Explained, The Book of Daniel, PBS Frontline, PBS.org
- ↑ According to historian Paul S. Boyer, "[Book of Danie] is dated by most scholars to the second century when Judea was once again under attack", When time shall be no more: prophecy belief in modern American culture By Paul S. Boyer, p. 26
- ↑ Brown, Raymond E.; Fitzmyer, Joseph A.; Murphy, Roland E., eds (1999). The New Jerome Biblical Commentary. Prentice Hall. p. 448. ISBN 0138598363. "Until relatively recent years Jews and Christians have considered Dn to be true history, containing genuine prophecy. [...] There would be few modern biblical scholars, however, who would now seriously defend such an opinion. The arguments for a date shortly before the death of Antiochus IV Epiphanes in 164 are overwhelming."
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 John Joseph Collins, Peter W. Flint, Cameron VanEpps, The Book of Daniel: Composition and reception, BRILL, 2002, ISBN 0391041282, p. 341.
- ↑ Mark Mangano, Esther/Daniel, College Press, 2001, ISBN 0899008852, p. 18.
- ↑ Collins, John J. (2002). Collins, John J.; Flint, Peter W.. eds. The Book of Daniel: Composition and Reception (Supplements to Vetus Testamentum). 1. Brill Academic Publisher. p. 2. ISBN 9004116753. "Fundamentalist readings of Daniel continue to flourish in the popular culture, as can be seen from the best-selling writings of Hal Lindsey, and conservative scholars have continued to fight rear-guard actions in defence of the reliability of the book. In mainline scholarship, however, the great issues that made Daniel the focus of controversy for centuries were laid to rest in the late 19th and early 20th century. A broad consensus on several key issues has existed since then. It is agreed that Daniel is pseudoepigraphic: the stories in chapters 1-6 are legendary in character and the visions in chapters 7-12 were composed by persons unknown in the Maccabean era."
- ↑ Notes 1992, p. 1021
- ↑ Shea 1986
- ↑ Casey 1980
- ↑ Ford 1978 Ford speaks of 'the almost universal application of [the little horn symbol of chapter 8] to Antiochus Epiphanes'. He also quotes the pre-critical and post-counter reformation view of the Anglican Bishop Thomas Newton in his "Dissertation on the Prophecies..." originally published in the mid 1700s (JF Dove,1838, p247): 'This little horn [of Daniel 8] is by the generality of interpreters, both Jewish and Christian, ancient and modern, supposed to mean Antiochus Epiphanes.' Newton adds that 'most of the ancient fathers and modern divines and commentators' agree with Jerome in identifying Antiochus in chapter 8, while also allowing that "Antiochus Epiphanes was a type of Antichrist".
- ↑ Rowley 1950, p. 158
- ↑ Dougherty 1929, p. 199
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 van den Heuvel 1998
- ↑ Collins 1994, p. 30
- ↑ Wiseman, D. J. (November 25, 1957). Darius the Mede. Christianity Today. pp. 7–10.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Miller 1994, p. 149
- ↑ e.g., as stated in Hippolytus' Diamerismos, §204, among other places.
- ↑ Colless 1992, p. 115
- ↑ Lendering, Jona. "Cyrus takes Babylon: the Nabonidus chronicle". self published. http://www.livius.org/ct-cz/cyrus_I/babylon02.html. Retrieved 2010-06-12.
- ↑ Collins 1994, p. 32
- ↑ Xenophon
- ↑ Lenci 2008
- ↑ Hasel 1977, p. 168, note 91
- ↑ Wilson 1917, p. 107-111
- ↑ Shea 1982, p. 148-9
- ↑ Millard 1977, p. 71
- ↑ Young 2009, p. 115
- ↑ Lendering, Jona. "Cyrus takes Babylon: Daniel & Prayer of Nabonidus". self published. http://www.livius.org/ct-cz/cyrus_I/babylon04.html. Retrieved 2010-06-21.
- ↑ Peter W. Flint, The Daniel Tradition at Qumran, in Collins et al. (2002), p.336.
- ↑ Steinmann, A. (December 2002). "The Chicken and the Egg: A New Proposal for the Relationship between the "Prayer of Nabonidus" and the "Book of Daniel"". Revue de Qumran 20 (4): 557–570.
- ↑ Gaston 2009, pp. 47–52
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 {{|Collins|1994|p=217-218}}
- ↑ The Madness of King Nebuchadnezzar..., Leiden, Brill, 1999
- ↑ Horn, Siegfried H. (April 1978). "New Light on Nebuchadnezzar's Madness" (pdf). Ministry Magazine. pp. 38–40. http://www.ministrymagazine.org/archives/1978/MIN1978-04.pdf. Retrieved 2010-06-22.
- ↑ Gaston 2009, pp. 58–61
- ↑ Gaston 2009, pp. 19–34
- ↑ Studies on the Hasmonean period, Joshua Efrón, 59
- ↑ Oppenheim 1966, p. 308
- ↑ Carey 1999, p. 42
- ↑ Boyer 1992, p. 26
- ↑ Cohn-Sherbok 1996, p. 209
- ↑ Hoppe 1992, p. 209
- ↑ Tomasino 2003, p. 18
- ↑ Murphy 1998, p. 436
- ↑ Barton 2009, p. 299
- ↑ Goldingay 1989
- ↑ Lendering, Jona. "Alexander visits Jerusalem". self published. http://www.livius.org/aj-al/alexander/alexander_t35.html. Retrieved 2010-06-28.
- ↑ Schwartz 1992, p. 110
- ↑ Grabbe 2008, p. 287
- ↑ Shaye Cohen, "Alexander the Great and Jaddus the High Priest according to Josephus", Association for Jewish Studies Review 7-8 (1982-1983) 41-68; see also Adolf Büchler,"La relation de Josephe concernant Alexandre le Grand", 1-26
- ↑ Christian Thinktank; http://www.christian-thinktank.com/qwhendan3a.html; Was Daniel Written After the Events he Foretold?; December 2000
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 54.2 The Dating of the Book of Daniel, Bryan Rennie
- ↑ Tanakh and its Shape
- ↑ Between the Testaments, David Syme Russell
- ↑ Eerdmans dictionary of the Bible By David Noel Freedman, Allen C. Myers, Astrid B. Beck, p. 311. NIV footnote on Ezekiel 14:14
- ↑ Who is Ezekiel's Daniel? | Bible.org - Worlds Largest Bible Study Site
- ↑ "Septuagint" Encyclopædia Britannica Online
- ↑ Introducing the Old Testament By John William Drane, John Drane, pp. 221-222
- ↑ Introduction to the Bible By John Haralson Hayes, pp 285-286
- ↑ Casey P.M, Porphyry and the origin of the Book of Daniel, Journal of Theological Studies, 1976, pp. 15-33
- ↑ Horrible abomination: šiqqǔṣ šômēm in the original Hebrew, a contemptuous pun on the title 'baal hashshamayim' (Lord of heaven), title of the Semitic storm god Hadad with whom Zeus Olympius had been identified. cf. e.g., J.A. Montgomery, Daniel, p. 388
- ↑ Interpreting the Bible: a handbook of terms and methods, W. Randolph Tate, [1]
- ↑ The Peshiṭta of Daniel, Richard A. Taylor, pp. 200-201
- ↑ A short introduction to the Hebrew Bible, John J. Collins, p. 282
- ↑ New American Bible, Daniel 7
- ↑ Sibylline Oracles 4, 49-101; Polybius, 38.22; Velleius Paterculus 1.6.6; Tacitus, Histories, 5.8.4, Diodorus 32.24 and Appian, Lybica 132.
- ↑ New American Bible, Daniel 6
- ↑ Livius.org
- ↑ Smith, U., 1944, Daniel and Revelation, Southern Publishing Association, Nashvill, TN
- ↑ Anderson, A., 1975, Pacific PRess Pub. Assoc., Unfolding Daniel's Prophecies, Mountain View, CA
- ↑ Daniel 7:13-27 see verses 13, 14, 22, 27
- ↑ "The Four Kingdoms Of Daniel" by John H. Walton, Journal of the Evangelical Theological Society 29.1 (1986): 25-36.
- ↑ Hartman and Di Lella, (1990), 408.
- ↑ Daniel, Hermeneia Commentary
- ↑ 2 "The Skeptical Review Online". http://www.infidels.org/library/magazines/tsr/2001/3/013mail.html 2.
- ↑ "There is no possibility that the text of Daniel could have been composed as late as the Maccabean uprising, and that there is every likelihood that the Aramaic comes from the same period, if not a century earlier, than the Aramaic of the Elephantine Papyri and of Ezra, which are admittedly fifth-century productions. It goes without saying that if the predictions concerning the period of Antiochus III and Antiochus IV (222-164 BCE) are composed in language antedating the second-century and third-century B.C., then the whole effort to explain Daniel as a vaticinium ex eventu must be abandoned."
- ↑ E.C. Lucas, Daniel (Apollos OT Commentary; Apollos, 2002) p. 307.
- ↑ Guthrie, Kenneth Sylvan; Fideler, David R (1987). The Pythagorean Sourcebook and Library. ISBN 9780933999510. http://books.google.com/?id=EigQoSZCUAwC&pg=PA334&lpg=PA334&dq=symphonia+GREEK+PYTHAGORAS.
- ↑ Stimilli, Davide (2005). The Face of Immortality: Physiognomy and Criticism. ISBN 9780791462638. http://books.google.com/?id=dyC1LXCx73QC&pg=PA30&lpg=PA30&dq=symphonia+GREEK+PYTHAGORAS.
- ↑ Frank E. Gaebelein, The Expositor's Bible Commentary, Vol. 7, Zondervan, 1985, p. 21.
- ↑ John E. Goldingay, Daniel, (Word Biblical Commentary, 30; Dallas: Word Books, 1989), p. xxv.
- ↑ Evans, Craig A.; Flint, Peter W. (1997). Eschatology, messianism, and the Dead Sea scrolls. Grand Rapids, Mich.: W.B. Eerdmans. ISBN 978-0-8028-4230-5. http://books.google.com/?id=DDUw9mvbq4AC&pg=PA44.
- ↑ Eerdmans dictionary of the Bible By David Noel Freedman, Allen C. Myers, Astrid B. Beck
- ↑ Invitation to the Apocrypha By Daniel J. Harrington
- ↑ Deuterocanonicals/Apocrypha By Watson E. Mills, Richard F. Wilson
- ↑ Eerdmans commentary on the Bible By James D. G. Dunn, John William Rogerson
- ↑ Sanford LA Sor, William; Sor, William Sanford, La; Hubbard, David Allan; Bush, Frederic William; Allen, Leslie C.; Sanford Lasor, William (1996). Old Testament survey: the message, form, and background of the Old Testament. Grand Rapids, Mich.: W.B. Eerdmans. p. 574. ISBN 978-0-8028-3788-2. http://books.google.com/?id=6wSWpZmmlAoC&pg=PA574.
- ↑ Parallel translations of Daniel 7:13
- ↑ Bromiley, Geoffrey W. (1995). International Standard Bible Encyclopedia: K-P Volume 3 of The International Standard Bible Encyclopedia. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 800. ISBN 9780802837837. http://books.google.com/?id=r7QTYwYvvx0C&pg=PA800
- ↑ Collins, John Joseph; Flint, Peter W.; VanEpps, Cameron. (2001). The book of Daniel : composition and receptio. Leiden ; Boston: Brill. p. 543. ISBN 978-90-04-12202-4. http://books.google.com/?id=NuZlNCGRaPkC&pg=PA543.
- ↑ New American Bible
- ↑ Introducing the New Testament: its literature and theology, Paul J. Achtemeier, Joel B. Green, Marianne Meye Thompson
- ↑ An introduction to the New Testament and the origins of Christianity, Delbert Royce Burkett
- ↑ Reynolds, Benjamin E. (2008). The apocalyptic son of man in the gospel of John. Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck. p. 43. ISBN 978-3-16-149726-1. http://books.google.com/?id=S_lMRtGEuAsC&pg=PA43.
- ↑ Wright, N. T. (1992). Christian origins and the question of God. Minneapolis: Fortress Press. p. 316. ISBN 978-0-8006-2681-5. http://books.google.com/?id=PuTxOT4syCkC&pg=PA316.
- ↑ Craig Blomberg, Jesus and the Gospels, Apollos 1997, pp.322-326
- ↑ Wright, N. T. (1992). Christian origins and the question of God. Volume 2, Jesus and the victory of God. Minneapolis: Fortress Press. p. 352. ISBN 0-8006-2682-6. http://books.google.com/?id=ms-xtRQoLUIC&pg=PA352.
- ↑ Hartman and Di Lella, 1990, p. 419
- ↑ Encyclopedia of theology: the concise Sacramentum mundi, Karl Rahner
References
- Barton, John (2009) (Google On-line Books). The biblical world. 2. T & F Books. pp. 1152. ISBN B000SIWRPA. http://books.google.com/?id=eKHlH0nmzScC&pg=PA299. Retrieved 2010-06-26.
- Boyer, Paul S. (1992) (Google on-line books). When Time Shall Be No More: Prophecy Belief in Modern American Culture. Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. pp. 488. ISBN 0674951298. http://books.google.com/?id=FyTeW7vQ8K4C&dq=When+Time+Shall+be+No+More+By+Paul+S.+Boyer&printsec=frontcover. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- Briant, Pierre (1996). From Cyrus to Alexander. Librairie Artheme Fayard. Translation by Peter Daniels, 2002. Paris. p. 42. ISBN 1575060310.
- Carey, Greg (1999). Bloomquist, L. Gregory. ed (Google On-line Books). Vision and Persuasion: Rhetorical Dimensions of Apocalyptic Discourse. Chalice Press. p. 42. ISBN 0827240058. http://books.google.com/?id=NyGyGyhUtIEC&pg=PA42. Retrieved 2010-06-25.
- Casey, Maurice (1980). Son of Man: The interpretation and influence of Daniel 7. Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge. pp. 272. ISBN 0281036977. "lists ten commentators of the 'Syrian Tradition' who identify the fourth beast of chapter 7 as Greece, the little horn as Antiochus, and - in the majority of instances - the "saints of the Most High" as Maccabean Jews."
- Cohn-Sherbok, Dan (1996) (Google on-line books). The Hebrew Bible. Cassell. pp. 257. ISBN 030433703X. http://books.google.com/?id=esHK1XA7_8UC&pg=PA209. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- Colless, Brian (1992). "Cyrus the Persian as Darius the Mede in the Book of Daniel" (pdf). Journal for the Study of the Old Testament (subscription site) 56: 115. http://jot.sagepub.com/cgi/pdf_extract/17/56/113?ck=nck. Retrieved 2010-06-12.
- Collins, John Joseph (1994). Daniel: A Commentary on the Book of Daniel (Hermeneia: a Critical and Historical Commentary on the Bible). Augsburg Fortress Publishers. pp. 499. ISBN 0800660404.
- Dougherty, Raymond Philip (1929). Nabonidus and Belshazzar: A Study of the Closing Events of the Neo- Babylonian Empire. Yale University Press. pp. 216. ISBN B000M9MGX8.
- Easton's Bible dictionary
- Robert Eisenman, James the Brother of Jesus, 1997. ISBN 0-14-025773-X.
- Ford, Desmond (1978). Daniel. Southern Publishing Association. pp. 309. ISBN 0812701747.
- Gaston, T. E. (2009). Historical Issues in the Book of Daniel. TAANATHSHILOH. pp. 178. ISBN 095615400X.
- Goldingay, John (1989) (Rich text format of book). Daniel (Word Biblical Themes). Dallas: Word Publishing Group. pp. 132. ISBN 0849907942. http://documents.fuller.edu/sot/faculty/goldingay/cp_content/homepage/TheTheologyoftheBookofDaniel.rtf. Retrieved 2010-06-28.
- Grabbe, Lester L. (2008). "Chapter 16: Israel from the Rise of Hellenism to 70 CE". In Rogerson, John William; Lieu, Judith (Google On-line Books). The Oxford handbook of biblical studies. USA: Oxford University Press. pp. 920. ISBN 0199237778. http://books.google.ca/books?id=HMkMeaijNT4C&pg=PA287. Retrieved 2010-06-28.
- Louis F. Hartman and Alexander A. Di Lella, "Daniel", in Raymond E. Brown et al., ed., The New Jerome Biblical Commentary, 1990, pp. 406–20.
- Hasel, Gerhard Franz (1977). "The First and Third Years of Belshazzar (Dan 7:1; 8:1)" (pdf). AUSS Journal Online Archive (Andrews University Seminary) 15: 153–168. http://www.auss.info/auss_publication.php?pub_id=564&journal=1&cmd=view&hash=. Retrieved 2010-06-18.
- Hoppe, Leslie J. (1992). "Deuteronomy". In Bergant, Dianne (Google On-line Books). The Collegeville Bible commentary: based on the New American Bible: Old Testament. Liturgical Press. pp. 464. ISBN 0814622119. http://books.google.com/?id=Nj-AkOJ9wRQC&pg=PA560. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- Ernest C. Lucas, Daniel, 2002. ISBN 0-85111-780-5.
- Keil, C. F.; Delitzsch, Franz (2006) [1955]. Ezekiel and Daniel. Commentary on the Old Testament. 9. Hendrickson Publishers. ISBN 0913573884.
- Lenci, Tosca (2008). "Appendix 3A. II, Descendancy Chart, Neo-Babylonians" (pdf). History of the Daughters (ebook). Sonoma, California: L P Publishing. ISBN 0966767861. http://www.historyofthedaughters.com/34.pdf. Retrieved 2010-06-18.
- Millard, Alan R. (Apr-June 1977). "Daniel 1-6 and History" (pdf). Evangelical Quarterly (Paternoster) 49 (2): 67–73. http://www.biblicalstudies.org.uk/pdf/eq/daniel1-6_millard.pdf. Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- Miller, Stephen B. (1994). Daniel. New American Commentary. 18. Nashville: Broadman and Holman. pp. 348. ISBN 0805401180.
- Murphy, Frederick James (1998) (Google On-line Books). Fallen is Babylon: the Revelation to John. Trinity Press International. pp. 472. ISBN 1563381524. http://books.google.com/?id=uZvGwtOaYNUC&pg=PA436. Retrieved 2010-06-26.
- Notes (1992). The New American Bible. Catholic Book Publishing Co.. p. 1021. ISBN 9780899425108.
- Oppenheim, A. Leo (1966). "Babylonian and Assyrian Historical Texts". In James B. Pritchard. Ancient Near Eastern Texts (2nd ed.; 3rd print ed.). Princeton University Press. p. 308.
- Rowley, H. H. (1950). The Growth of the Old Testament. Harper.
- Rowley, H. H. (1959). Darius the Mede and the Four World Empires in the Book of Daniel: A Historical Study of Contemporary Theories. University of Wales Press. pp. 195. ISBN 159752896X.
- Schwartz, Daniel R. (1992) (Google On-line Books). Studies in the Jewish background of Christianity. J.C.B. Mohr. pp. 304. ISBN 3161457986. http://books.google.com/?id=rd5OB4PtlCUC&pg=PA110. Retrieved 2010-06-28.
- Shea, William H. (1982). "Nabonidus, Belshazzar, and the Book of Daniel: An Update" (pdf). AUSS Journal Online Archive (Andrews University Seminary) 20 (2): 133–149.. http://www.auss.info/auss_publication_file.php?pub_id=649&journal=1&type=pdf. Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- Shea, William H. (1986). "The Prophecy of Daniel 9:24-27". In Holbrook, Frank. The Seventy Weeks, Leviticus, and the Nature of Prophecy. Daniel and Revelation Committee Series. 3. Review and Herald Publishing Association.
- Tomasino, Anthony J. (2003). Judaism before Jesus: the ideas and events that shaped the New Testament world. IVP Academic; Print On Demand Edition. pp. 345. ISBN 0830827307. http://books.google.com/?id=AwTobS58tZwC&pg=PA18. Retrieved 2010-06-26.
- van den Heuvel, Curt (1998). "Revealing Daniel". self published. http://www.2think.org/hundredsheep/bible/comment/daniel.shtml#8-1. Retrieved 2010-06-09.
- VanderKam, James C; Flint, Peter (2004) (online). The Meaning of the Dead Sea Scrolls: Their Significance For Understanding the Bible, Judaism, Jesus, and Christianity. London: T & T Clark International. ISBN 9780567084682. http://books.google.com/?id=SBMXnB4CRpUC&pg=PA137. Retrieved 2010-06-09.
- Wilson, Robert Dick (1917). Studies In The Book Of Daniel: A Discussion Of The Historical Questions. G. P. Putnam's Sons. pp. 408. ISBN 143726462X.
- Wiseman, D. J. (1965). Notes on Some Problems in the Book of Daniel. London: Tyndale Press. pp. 80. ISBN 085111038X.
- Xenophon. "5". Cyropaedia. 7. Perseus Digital Library. 28-30. ISBN 1419114859. http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.01.0204%3Abook%3D7%3Achapter%3D5%3Asection%3D28.
- Young, Edward J. (2009) [1949]. The Prophecy of Daniel: a Commentary. Eerdmans Publishing. pp. 332. ISBN 0802863310.
Further reading
- Bickerman, E. J. (1967). Four Strange Books of the Bible, 1967. ISBN 0-8052-0774-0.
- Hebbard, Aaron. "Reading Daniel as a Text in Theological Hermeneutics." Eugene: Pickwick, 2009. ISBN 1-55635-991-8.
- DiTommaso, Lorenzo (2005). The Book of Daniel and the Apocryphal Daniel Literature. Studia in Veteris Testamenti pseudepigrapha 20. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 9004144129.
- Niskanen, Paul (2004). The Human and the Devine in History: Herodotus and the Book of Daniel. Journal for the study of the Old Testament. Supplementary series. London, et al.. ISBN 03090787.
- W. Sibley Towner, "Daniel", in The Oxford Companion to the Bible, 1993, pp. 149–52.
- John F. Walvoord, Daniel: The Key to Prophetic Revelation, 1989. ISBN 0-8024-1753-1.
- Woude, A.S. van der, ed (1993). The Book of Daniel in the Light of New Findings. Bibliotheca ephemeridum theologicarum Lovaniensium 106. Louvain. ISBN 906831467X.
External links
Jewish translations
- Daniel (Judaica Press) * translation [with Rashi's commentary] at Chabad.org
Christian translations
- Daniel at The Great Books * (New Revised Standard Version)
- The Book of Daniel * (Full text from St-Takla.org, also available in Arabic)
Related articles
- Daniel at iTanakh
- Jewish Encyclopedia: Daniel
- Daniel: Wise Man and Visionary, by Elias Bickerman
- Daniel by Rob Bradshaw Detailed dictionary-style article.
| Preceded by Esther |
Hebrew Bible | Followed by Ezra-Nehemiah |
| Preceded by Ezekiel |
Christian Old Testament | Followed by Hosea |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

